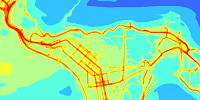
- Overview
- Air pollution modelling
- ADMS 6
- ADMS-Roads (Extra)
- ADMS-Urban
- MAQS
- ADMS-Airport
- ADMS-Screen
- Feature comparison
- Emissions management
- EMIT
- Wind energy and airflow
- FLOWSTAR-Energy
- Accidental releases
- GASTAR
- LSMS
- ADMS-Puff
- ADMS-STAR
- Managing model runs
- Run Manager
- Model evaluation
- Model Evaluation Toolkit
- Meteorological data processing
- WRFtoMet
- Related Documentation
- User guides
- Technical specifications
- Model validation
- Newsletters
- Publications
- CERC co-author publications
- CERC software publications
- Presentations
- Other information
- Traffic emissions
- Prices
- Free demo
- Visualisation tools
- Current software versions
- System requirements


ADMS 6
World leading software for modelling industrial air pollution
What is ADMS 6?

ADMS 6 is an advanced dispersion model used to model the air quality impact of existing and proposed industrial installations. It was originally developed for regulatory authorities in the UK. Its many features include allowance for the impacts of buildings, complex terrain, coastlines and variations in surface roughness; dry and wet deposition; NOx chemistry schemes; chemical reactions of amines released during carbon capture and storage (CCS); short term releases (puffs); calculation of fluctuations of concentration on short timescales, odours and condensed plume visibility; and allowance for radioactive decay including γ-ray dose.
Typical applications include:
- assessment of modelled air pollution concentrations against air quality standards and limit values including those from WHO, EU, UK, USA and China,
- planning/permitting, e.g. under Industrial Emissions Directive or Environmental Permitting Regulations,
- stack height determination,
- odour modelling,
- environmental impact assessments and
- safety and emergency planning.
Who uses ADMS 6?
The dispersion model ADMS 6 is currently used in many countries worldwide. Users of ADMS 6 include:
- over 130 individual company licence holders in the United Kingdom,
- regulatory authorities including the UK Health and Safety Executive (HSE),
- Environment Agency in England,
- Scottish Environmental Protection Agency (SEPA) in Scotland,
- Northern Ireland Environment Agency (NIEA) in Northern Ireland,
- Natural Resources Wales,
- government organisations including the Food Standards Agency (United Kingdom),
- users across Europe, Asia, Australia, North America, Africa and the Middle East.
Why use ADMS 6?
ADMS 6 is a new generation Gaussian plume air dispersion model, which means that the atmospheric boundary layer properties are characterised by two parameters:
- the boundary layer depth, and
- the Monin-Obukhov length
rather than in terms of the single parameter Pasquill-Gifford class.
Dispersion under convective meteorological conditions uses a skewed Gaussian concentration distribution (shown by validation studies to be a better representation than a symmetrical Gaussian expression).
The ADMS 6 model includes:
| Model options | ADMS 6 has a number of model options including: dry and wet deposition; NOx chemistry; impacts of hills, variable roughness, buildings and coastlines; puffs; fluctuations; odours; radioactivity decay (and γ-ray dose); condensed plume visibility; time varying sources and inclusion of background concentrations. |
|---|---|
| Meteorological pre-processor | ADMS 6 has an in-built meteorological pre-processor that allows flexible input meteorological data both standard and more specialist. Hourly sequential and statistical data can be processed, and all input and output meteorological variables are written to a file after processing. |
| User-defined outputs | The user defines the pollutant, averaging time (which may be an annual average or a shorter period), which percentiles and exceedence values to calculate, whether a rolling average is required or not and the output units. The output options are designed to be flexible to cater for the variety of air quality limits, which can vary from country to country, and are subject to revision. |
| Visualisation | ADMS 6 includes the Mapper: an integrated mapping tool for displaying and editing source data, buildings and receptor locations and viewing results. The model has links to the Surfer contour-plotting package, in addition to ArcGIS and MapInfo Professional Geographical Information System (GIS) software. The GIS links can be used to enter and display input data, and display output, usually as colour contour plots. |
| Terrain converter | Utilities are available for creating terrain files from commonly available data formats such as SRTM and OS Terrain 50. |
ADMS features contrasted with US-EPA model AERMOD
| ADMS 6 | AERMOD | |
|---|---|---|
| Meteorology | ||
| Meteorological pre-processor |  |
 |
| Dispersion | ||
| Boundary-layer structure | h, LMO scaling | h, LMO scaling |
| Plume rise | Advanced integral model | Briggs empirical expressions |
| Concentration distribution | Advanced Gaussian | Advanced Gaussian |
| Complex effects | ||
| Buildings | ADMS buildings module1 | PRIME buildings module1 |
| Complex terrain | Based on calculation of flow field and turbulence field by FLOWSTAR model | Interpolation between plume displaced by terrain height (neutral) and plume impaction (no vertical displacement, stable) |
| Deposition (wet and dry) |  |
 |
| Chemistry | Reaction of NO with O3, photolysis of NO2, amine chemistry2 | variety of NOx methods |
| Other options | ||
| Amine chemistry for carbon capture applications |  |
 |
| Modelling the effect of wind turbines on dispersion |  |
 |
| Concentration fluctuations |  |
 |
| Visible plumes | Condensed plume visibility |  |
| Temperature and humidity | In-plume temperature and humidity output |  |
| Radioactivity | Radioactive decay / γ-ray dose; decay chain database | Simple decay |
| Puff model |  |
 |
| Coastline module |  |
 |
| Marine boundary layer |  |
 |
| Input of vertical profiles of meteorological data |  |
 |
1 See A. Robins,2000:A discussion of the building modules in ADMS 3 and PRIME.(.pdf, <1MB)
2 The Amine chemistry module for modelling chemical reactions of amines released during carbon capture and storage (CCS) is not included in the standard model.
