
- Overview
- Net Zero and climate change
- Industrial permitting and planning
- Low Emission Zones and Low Traffic Neighbourhoods
- Air Quality Management
- Planning and development control
- Hazardous releases
- Odours
- Wind energy and airflow
- Urban environment and climate change
- Emissions inventories and emissions verification/ optimisation
- Model evaluation
- Aviation and air quality
Urban environment and climate change

Temperature variations relative to ambient (įC)
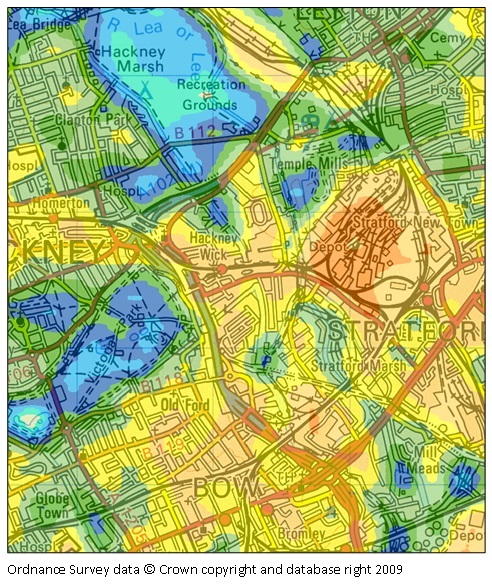
Local temperature variations on a late summer afternoon
With climate change and rapid urbanisation, the influence of the built environment on local temperature and humidity levels is of increasing interest. Policy makers and planners must consider mitigation strategies for urban heat islands that develop during the summer months and make life uncomfortable for residents of cities worldwide.
For tackling these problems, our consultants use our ADMS Temperature and Humidity model to investigate the impact of urban land use and morphology, and anthropogenic activities, on local temperatures and answer such questions as:
- What is the impact on the local climate of converting this green space into housing (or vice versa)?
- How effective are green and cool roofs on reducing local temperatures?
- What impact does the building fabric and reflectivity have on the local climate?
CERCís expertise in this field has led to a number of collaborations where the model has been used to develop urban heat island maps of cities including Beijing (China), Kuala Lumpur (Malaysia), parts of London (UK) and Birmingham (UK). In an ongoing NERC-funded project, the University of Birmingham are generating urban heat island maps for using within a Climate Risk and Vulnerability Assessment (CRVA) tool.
